Understanding the Process of Metal Coil Slitting and Rewinding: A Comprehensive Guide
Sep 25,2025

Understanding the Process of Metal Coil Slitting and Rewinding: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Metal Coil Slitting and Rewinding
- 2. Importance of Slitting and Rewinding in Manufacturing
- 3. The Metal Coil Slitting Process
- 4. Types of Metal Coil Slitting Machines
- 5. Key Components of Slitting Machines
- 6. The Rewinding Process in Metal Processing
- 7. Common Applications of Slit Metal Coils
- 8. Challenges in Coil Slitting and Rewinding
- 9. Best Practices for Effective Coil Slitting and Rewinding
- 10. Conclusion
- 11. FAQs
1. Introduction to Metal Coil Slitting and Rewinding
Metal coil slitting and rewinding are critical processes in the manufacturing sector, particularly in industries that require precise metal strips for further production. Slitting involves cutting large rolls of metal into narrower widths, while rewinding refers to the process of winding these slits back onto smaller cores. The combination of these techniques enables manufacturers to create products that meet specific requirements for various applications, from automotive components to construction materials.
2. Importance of Slitting and Rewinding in Manufacturing
The relevance of slitting and rewinding in manufacturing cannot be overstated. These processes contribute to operational efficiency by ensuring that raw materials are tailored to meet the exact specifications of downstream applications. By transforming large metal coils into manageable sizes, manufacturers can minimize waste, improve handling, and streamline production lines. Moreover, precise slitting allows for better quality control, resulting in finished products that comply with industry standards.
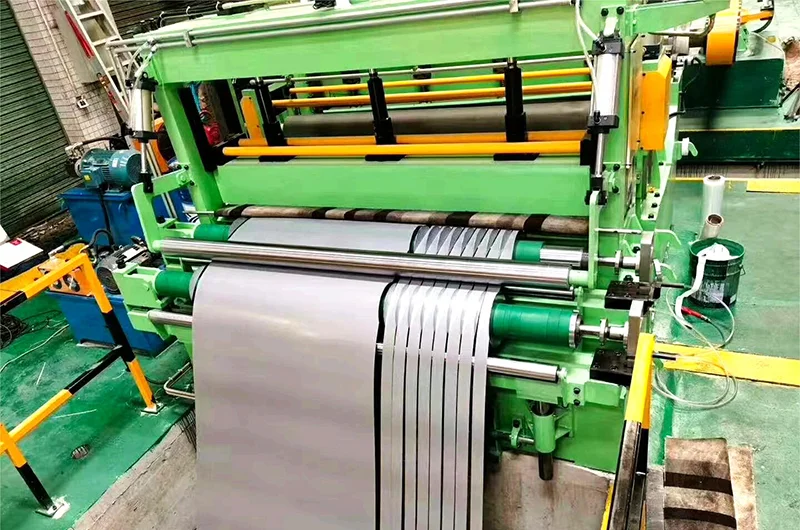
3. The Metal Coil Slitting Process
The metal coil slitting process involves several stages that ensure accuracy and efficiency:
3.1 Preparation of the Metal Coil
Before slitting can commence, the metal coil must be inspected and prepared. This involves checking the coil for defects, ensuring it is clean, and determining the appropriate width for slitting. Proper preparation is crucial as it sets the stage for a successful slitting operation.
3.2 Feeding the Coil into the Slitting Machine
Once prepared, the metal coil is fed into the slitting machine. This machine typically features a series of sharp blades that cut through the metal as it passes through. Operators must carefully align the coil to ensure that the cuts are uniform and meet the specified dimensions.
3.3 Slitting Operation
During the slitting operation, the machine's blades slice through the coil, creating narrower strips. These strips can vary in width depending on the production requirements. The slitting process can be adjusted to achieve different cutting patterns or to accommodate various metal thicknesses.
3.4 Quality Control Measures
Quality control is an integral part of the slitting process. Operators regularly monitor the cut strips for accuracy in width and thickness. Any deviations can lead to product rejection or rework, impacting overall efficiency.
3.5 Packaging and Preparation for Rewinding
After slitting, the strips are often packaged for transportation or further processing. However, many manufacturers choose to rewind the strips onto smaller cores for easier handling and storage.
4. Types of Metal Coil Slitting Machines
There are various types of metal coil slitting machines available, each designed for specific applications:
4.1 Rotary Slitting Machines
Rotary slitting machines are equipped with circular blades that rotate as the coil passes through. This type of machine is ideal for high-speed operations and can handle a variety of metal types.
4.2 Shear Slitting Machines
Shear slitting machines utilize a different mechanism where blades create a shearing action to cut through the metal. This type is often used for thicker materials and can provide clean cuts with minimal burrs.
4.3 Score Slitting Machines
Score slitting machines employ a scoring technique that compresses the metal before cutting. This method is efficient for producing strips with minimal deformation.
5. Key Components of Slitting Machines
Understanding the key components of slitting machines can enhance operational efficiency:
5.1 Blades
The blades are the heart of any slitting machine. They must be made from high-quality materials to withstand the stresses of cutting through metal.
5.2 Tensioning Systems
Tensioning systems maintain the correct tension on the metal coil as it passes through the machine, ensuring consistent cuts.
5.3 Alignment Guides
These guides help ensure that the coil is properly aligned during the slitting process, which is essential for achieving accurate widths.
5.4 Control Panels
Modern slitting machines are equipped with advanced control panels that allow operators to adjust settings, monitor performance, and maintain quality control throughout the process.
6. The Rewinding Process in Metal Processing
Rewinding is a crucial final step after slitting, where cut strips are wound onto smaller cores for convenient handling. This process can also involve:
6.1 Tension Control During Rewinding
Proper tension control during rewinding is vital to prevent coil deformation and ensure that the strips remain intact for further processing.
6.2 Packaging for Distribution
Once rewound, the metal coils are packaged securely for transport. Effective packaging is essential to protect the coils from damage and contamination during shipping.
7. Common Applications of Slit Metal Coils
Slit metal coils have a wide range of applications in various industries, including:
7.1 Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, slit metal coils are often used for manufacturing components such as brackets, frames, and body parts.
7.2 Construction
Construction materials such as metal roofing, siding, and HVAC ducts frequently utilize slit coils due to their durability and adaptability.
7.3 Consumer Goods
Many consumer products, from appliances to furniture, use slit metal components, showcasing the versatility of this manufacturing process.
8. Challenges in Coil Slitting and Rewinding
Despite its advantages, the metal coil slitting and rewinding process does encounter challenges:
8.1 Material Variability
Variability in metal properties may affect cutting precision and quality. Operators must adapt their techniques to accommodate different materials effectively.
8.2 Equipment Maintenance
Regular maintenance of slitting and rewinding machines is crucial to prevent downtime and ensure consistent performance. Neglecting maintenance can lead to equipment failures and increased operational costs.
8.3 Waste Management
Slitting operations can produce scrap metal, which requires effective management strategies to minimize waste and enhance sustainability.
9. Best Practices for Effective Coil Slitting and Rewinding
Implementing best practices can significantly enhance the efficiency and quality of slitting and rewinding operations:
9.1 Regular Training for Operators
Investing in regular training for operators ensures they are skilled in using the latest technology and techniques, leading to improved outcomes.
9.2 Continuous Quality Control
Establishing a robust quality control system helps catch defects early and reduces waste, ultimately improving the bottom line.
9.3 Invest in Advanced Technology
Utilizing state-of-the-art machinery and automation can optimize processes, reduce manual errors, and enhance production speed.
10. Conclusion
Understanding the process of metal coil slitting and rewinding is vital for any professional in the manufacturing sector. By mastering these techniques, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, reduce waste, and produce high-quality products tailored to customer specifications. As industries continue to evolve, staying informed about advancements in slitting and rewinding processes will be key to maintaining a competitive edge.
11. FAQs
1. What is the difference between slitting and rewinding?
Slitting involves cutting large metal coils into narrower strips, while rewinding refers to the process of winding these strips onto smaller cores for easier handling.
2. What types of materials can be slit using slitting machines?
Slitting machines can process various materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and other metals.
3. How can I ensure the quality of slit metal coils?
Implementing a robust quality control system, conducting regular inspections, and using reliable machinery can help ensure the quality of slit metal coils.
4. What are the common challenges faced in coil slitting?
Common challenges include material variability, equipment maintenance issues, and effective waste management.
5. How does automation impact the slitting and rewinding process?
Automation can significantly enhance efficiency, reduce manual errors, and increase production speed, leading to better overall outcomes.
PREVIOUS:
Articoli recenti